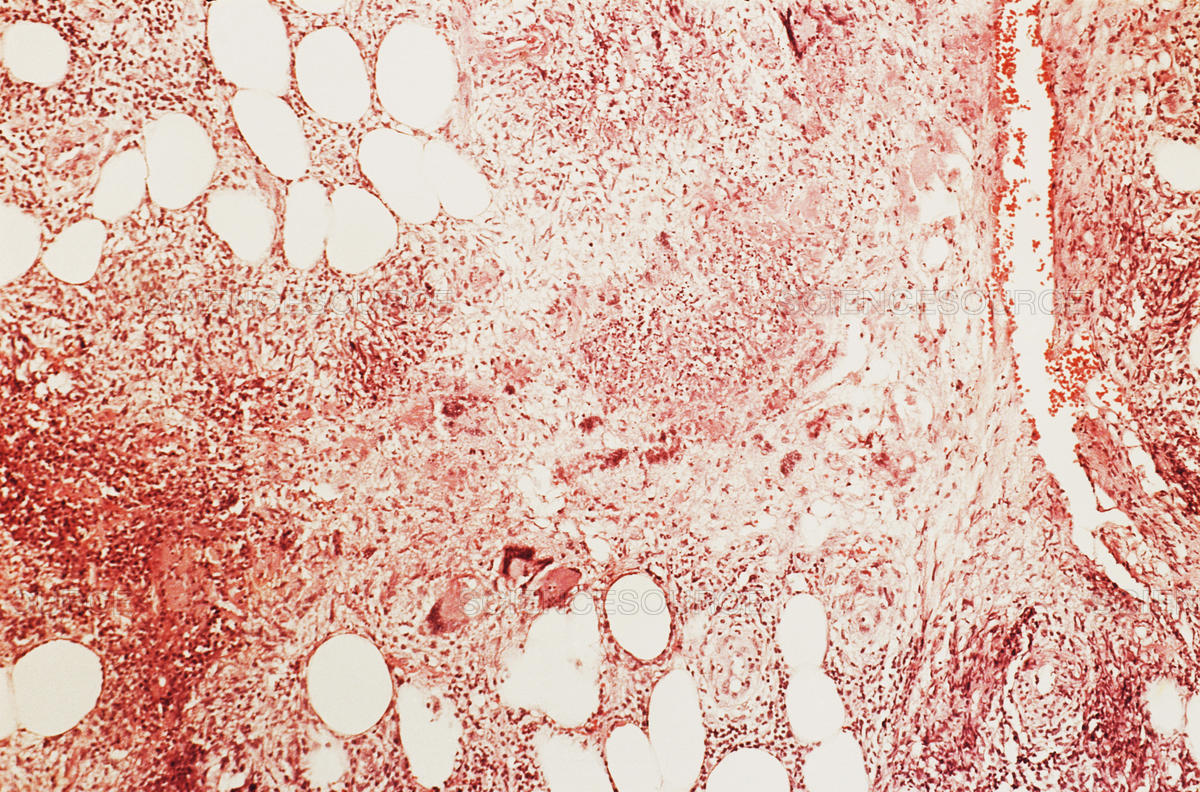
Subcutaneous fat cell inflammation, or erythema nodosum, is a severe disease that affects young women in particular. The disease is characterized by the appearance of subcutaneous nodules that are hot, red and sensitive in the front of the legs. In half of the cases of this disease, a relationship was found to be related to streptococcus infection, tuberculosis, pregnancy, (women) or chronic inflammatory bowel disease, as well as with receiving certain treatments (such as birth control pills, Sulfa drugs and Penicillin) ).
Treatment of symptoms of the disease depends on the use of drugs that prevent infections (anti-inflammatories that do not contain steroids - NSAIDs) and sometimes a corticosteroid may be used. The disease resolves after 6-8 weeks, except in rare cases in which the disease may be chronic with its exacerbation. Frequently.
Symptoms of erythema nodosum
An acute disease that affects young women in particular. It is characterized by the appearance of subcutaneous nodules that are hot, red and sensitive in the front of the legs.
Causes and risk factors of erythema nodosum
The disease may be related to infection with a nodular type of bacterial infection, and it may be related to tuberculosis, pregnancy or chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and it may also be related to the use of certain drugs (such as the contraceptive pill, sulfa and penicillin).
Treating knot erythema
Anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs) and corticosteroids are used to treat these conditions.
All sources from
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is an American nonprofit academic medical center currently based in three major locations: Rochester, Minnesota; Jacksonville, Florida; and Scottsdale, Arizona, focused on integrated patient care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff..
.png)
.png)